
Structure of Hydra. Crosssection of Hydra Polyp. Educational material
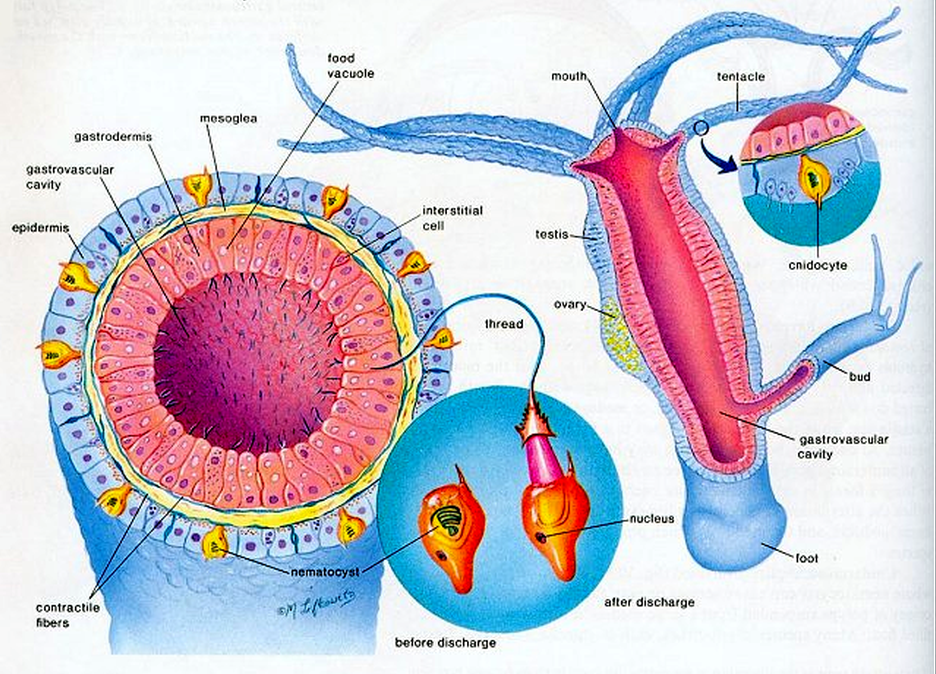
The body wall is comprised of two layers of cells separated by a thin, structureless layer of connective tissue called the mesoglea and the enteron, a cavity containing intestinal organs. The lower end of the body is closed, and an opening at the upper end both ingests food and ejects residue.

Anatomiestrukturschema Der Hydra Stock Vektor Art und mehr Bilder von
Structure of Hydra: Hydra has a slender tubular body and exhibits distinct radial symmetry (Fig. 12.2). The body is extremely contractile and the length varies from 10 to 30 mm. The lower end of the tubular body is closed and this side is designated as the aboral or proximal end. This end of the body is named as the foot or basal disc which is.
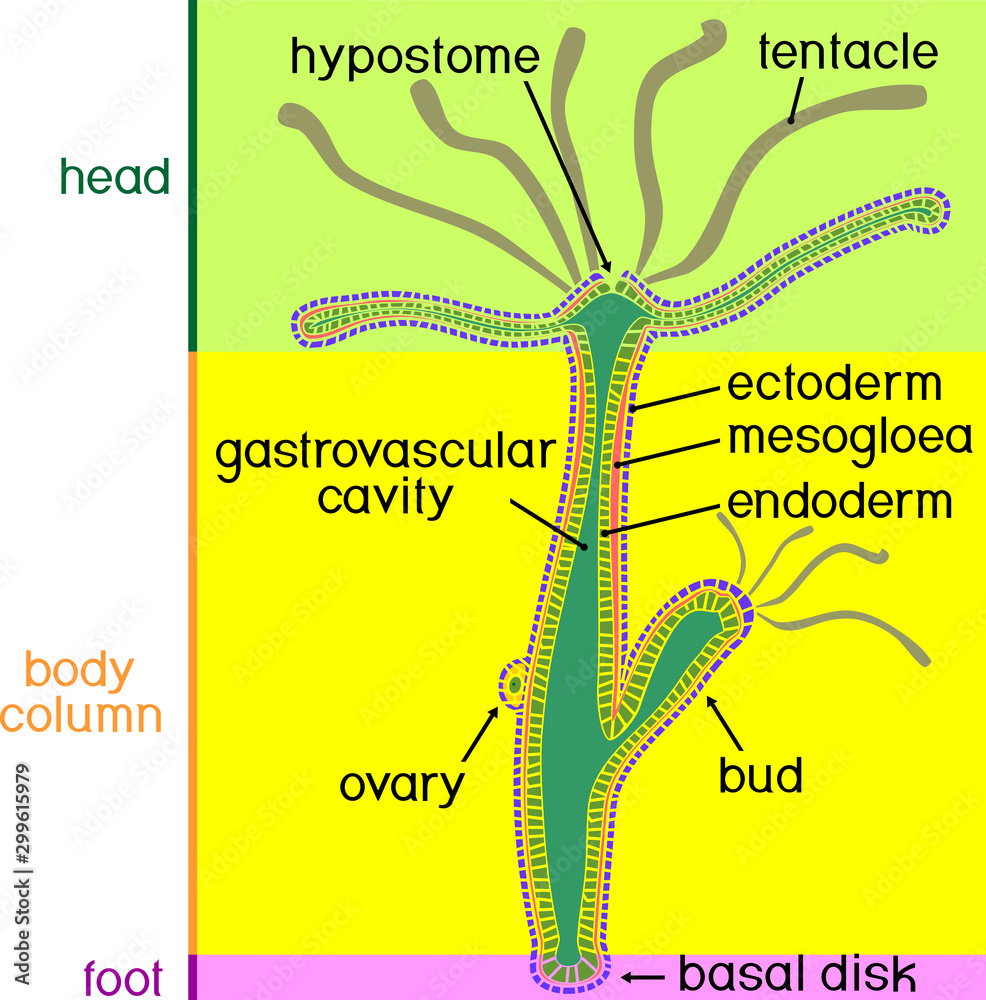
Structure of Hydra. Crosssection of Hydra Polyp. Educational material
Hydra, in Greek legend, the offspring of Typhon and Echidna (according to the early Greek poet Hesiod 's Theogony ), a gigantic water-snake-like monster with nine heads (the number varies), one of which was immortal.
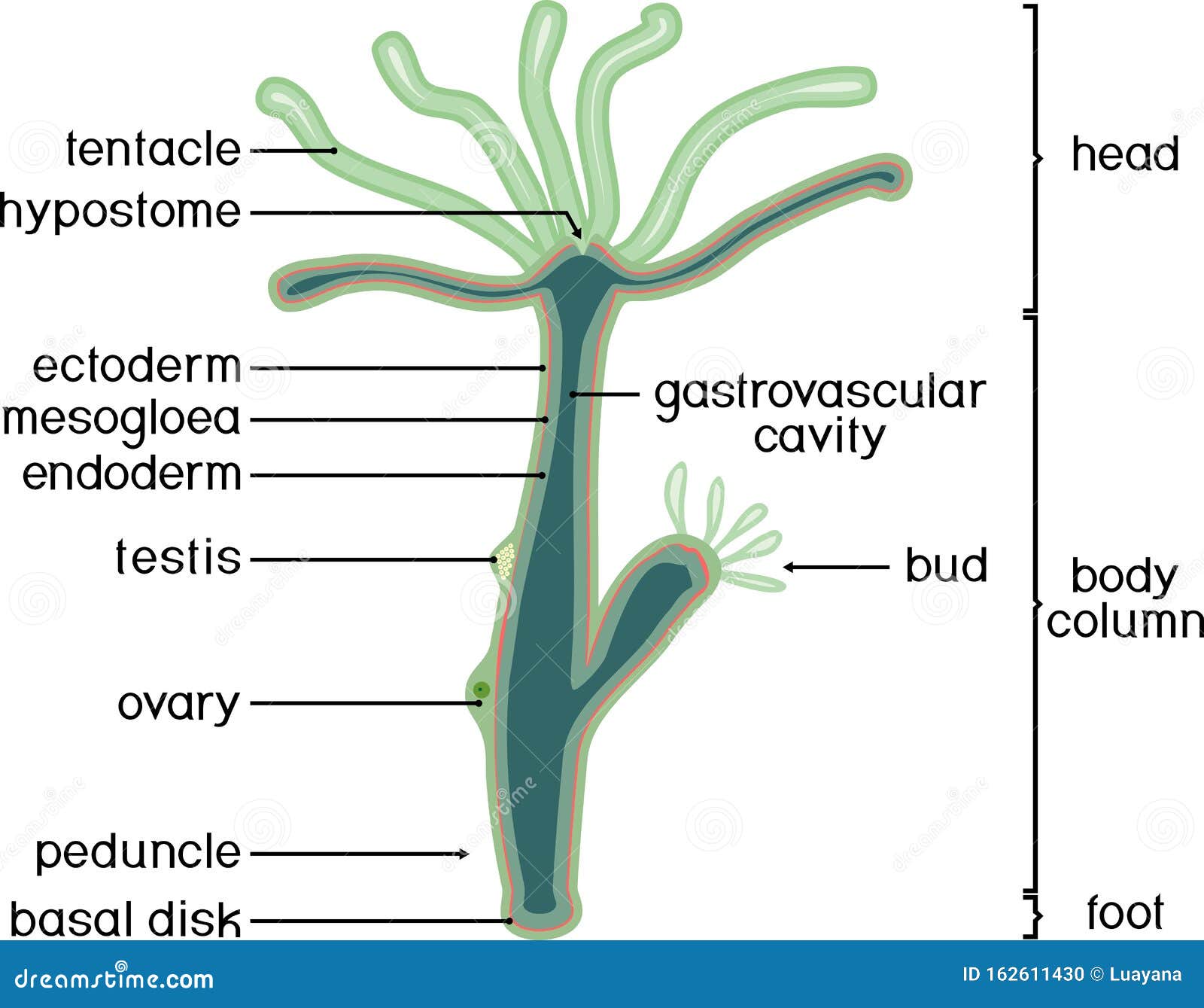
Structure of Hydra. stock vector. Illustration of mesoglea 162611430
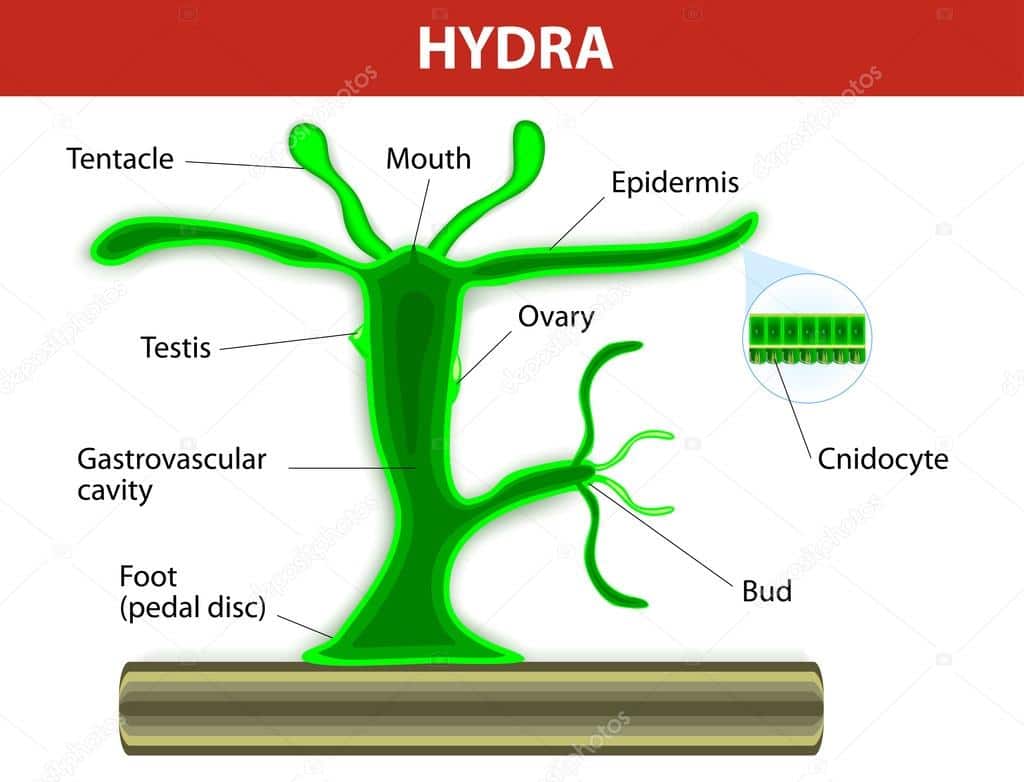
The hydra resembles a slender sea anemone. At the top of the organism is a number of tentacles arranged in a circle around the hydra's mouth. These tentacles are controlled by a simple neural net. Tiny stinging cells, called nematocysts, cover the tentacles. While harmless to humans, these cells can incapacitate the tiny organisms the hydra eats.
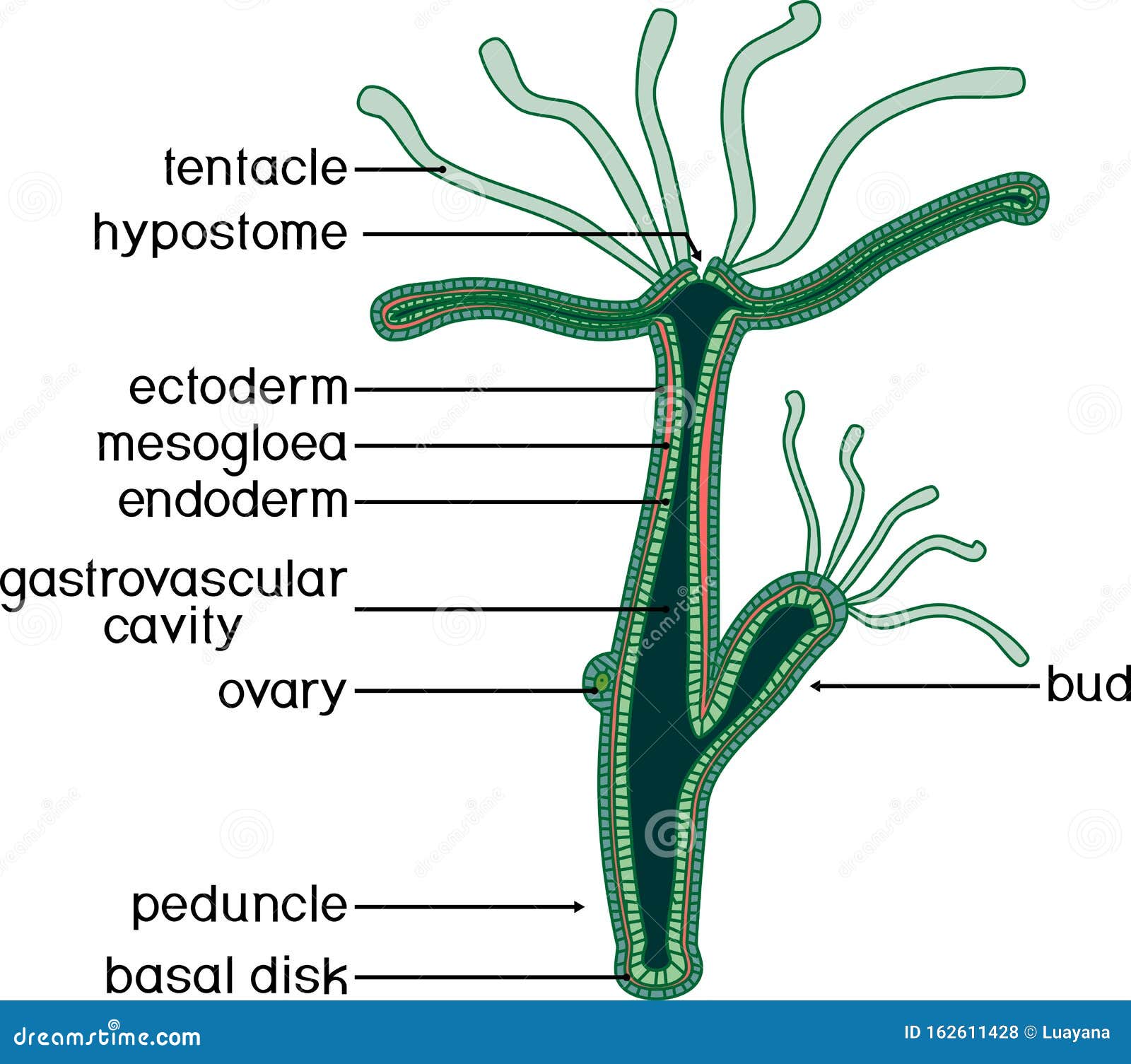
Structure of Hydra. stock vector. Illustration of cnidaria 162611428
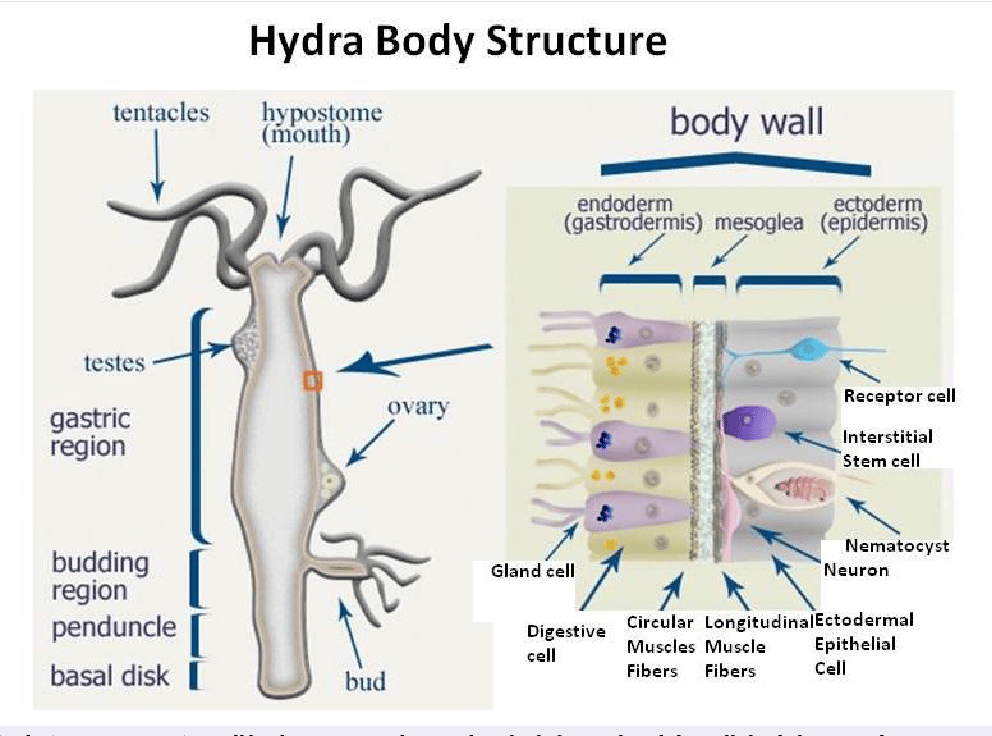
Structure In general, the body of a hydra is organized like a tube (polpy-like) with tentacles arranged around the head pole of the organism. A closer look, however, reveals a mouth opening (at the top pole of the organism surrounded by tentacles), a peduncle as well as a basal disk through which the organism attaches to the substrate.
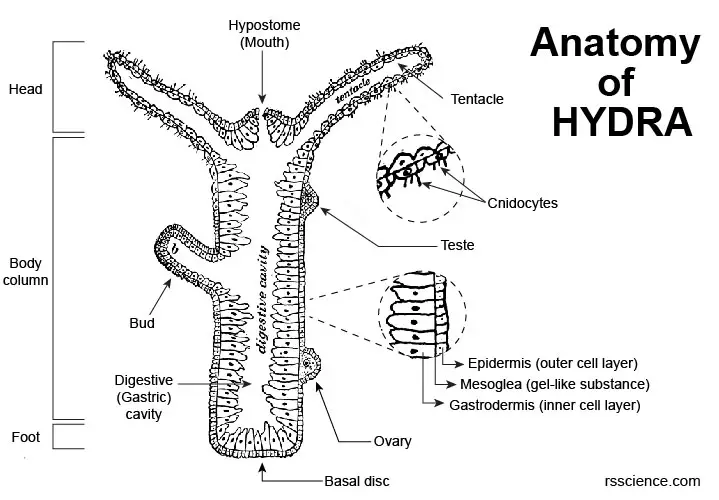
Hydra Biology, Classification, Characteristics, and Reproduction
Structure of Hydra Hydra is a type of invertebrate with the following structures: Tentacles: Hydras have long and slender tentacles that protrude from their body. These tentacles play a crucial role in their survival as they are used to capture food.

Anatomy Structure of Freshwater Hydra on White Background Stock Vector
1. It is a fresh water form cosmopolitan in distribution. ADVERTISEMENTS: 2. It is found attached to aquatic weeds. 3. Body differentiated into a long tubular trunk and a hypostome or mouth surrounded by a ring of long tentacles. 4. Through the body runs a cavity- the coelenteron which also extends into tentacles. 5.
Structure Of Hydra Parts And Functions
Structure of Hydra: Hydra belongs to the class Hydrozoa, Phylum cnidaria. 1. The body is more or less cylindrical (Fig. 20.1) and one end remains attached to a submerged object, wood or stone. 2. The attached end is known as the proximal end, the point of attachment is the pedal disc. 3.
Structure Of Hydra Parts And Functions
A quick overview Classification of Hydra - the Phylum Cnidaria Where does a Hydra Live? Is a Hydra Sensitive to Pollution? The Body Structure of Hydra Size and shape Color Body Foot Mouth Tentacles and Cnidocytes Nervous System How does a Hydra Hunt for Food? Hydra Symbiosis and Photosynthesis Can a Hydra Move? Looping Somersaulting

Photograph and diagram illustrating the anatomy of a hydra. Reproduced
Hydra Regeneration is a fascinating phenomenon that allows these animals to regenerate their entire body within a few days. This article reviews the cellular and molecular mechanisms that underlie this process, and how they relate to the evolution of stem cells and tissue regeneration in other organisms.

Structure of Hydra. Crosssection of Hydra Polyp. Educational material
The body wall of Hydra is organized as an epithelial bilayer (ectoderm and endoderm) with an intervening extracellular matrix (ECM), termed mesoglea by early biologists. Morphological studies have determined that Hydra ECM is composed of two basal lamina layers positioned at the base of each epithelial layer with an intervening interstitial matrix.
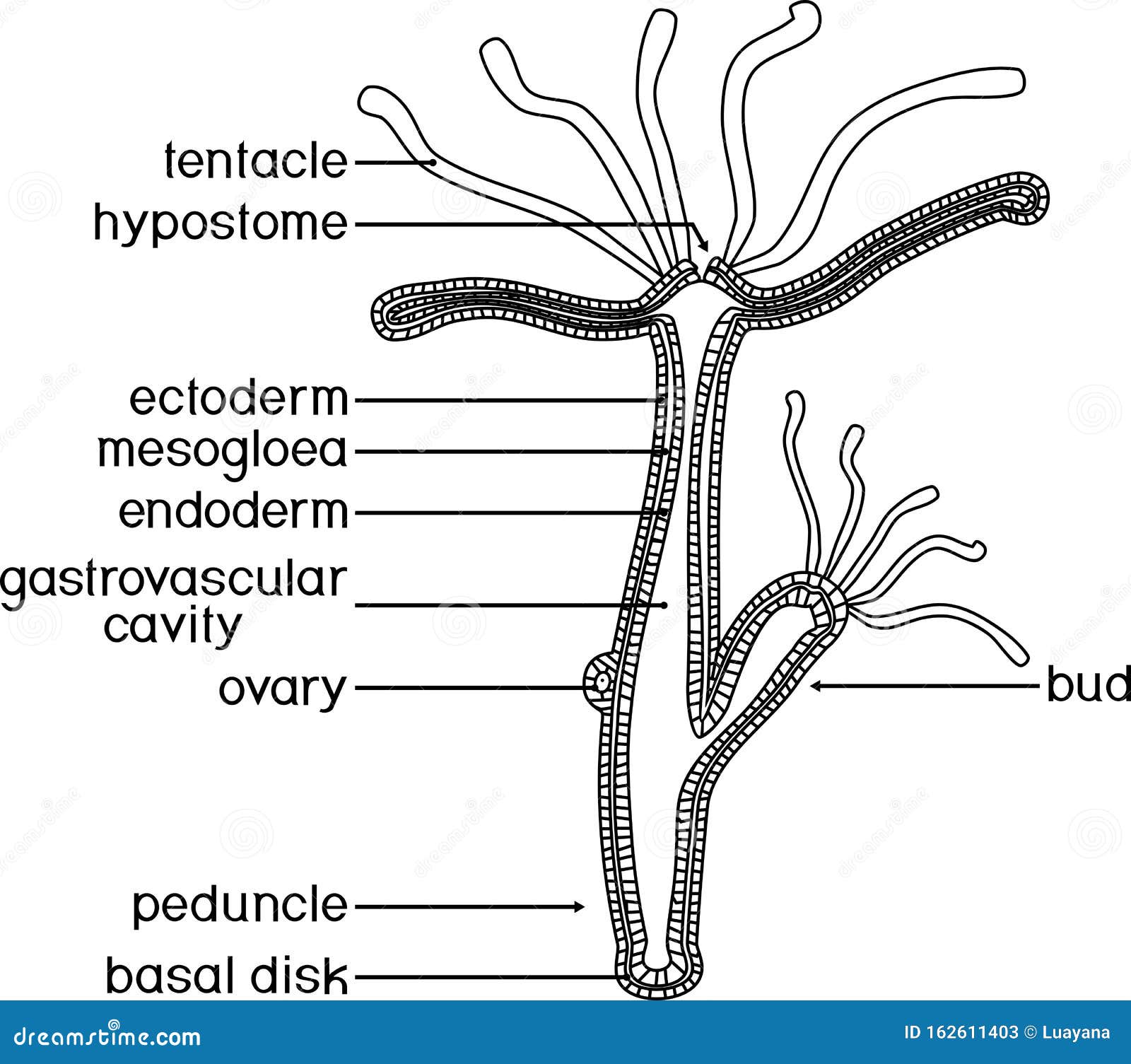
Structure of Hydra. stock vector. Illustration of contour 162611403
Internal structures Gastrovascular cavity Body wall (Histology) A. Epidermis 1. Epithelial muscle cells Functions 2. Gland cells Functions 3. Interstitial cells Functions 4. Cnidoblasts Functions Nematocysts I. structures of a cnidoblast II. Occurrence of Nematocysts III. Mechanism of Discharge IV. Types of Nematocysts 5. Sensory cells 6.
Hydra Octopus of the Microscopic World Useful In Medical Research
#hydra#morphologyofhydraIn this video we talk about the morphology of hydra.Hydra belongs to phylum coelentrata and is constituted by several species all ove.

Labelled diagram of hydra Brainly.in
In this article we will discuss about Hydra:- 1. History of Hydra 2. Habit, Habitat and Culture of Hydra 3. Structure 4. Locomotion 5. Nutrition 6. Respiration, Excretion and Osmoregulation 7. Nervous System 8. Behaviour 9. Reproduction 10. Regeneration 11. Immortality 12. Symbiosis 13. Physiological Division of Labour. Contents: History of Hydra
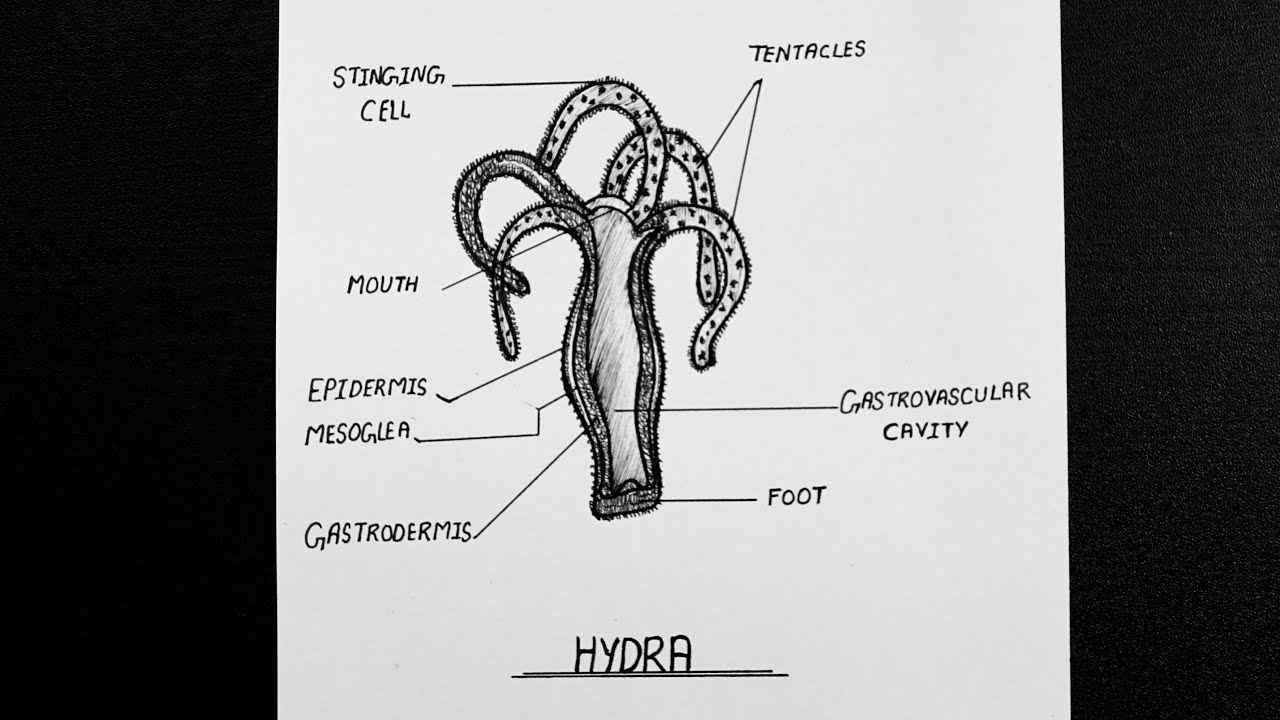
How To Draw Hydra Hydra Diagram How To Draw Label Hydra NCERT
Sections of hydra studied with the electron microscope show various structures which have been identified by referring to control histological sections and to previous descriptions. Certain features have also been examined in frozen-dried sections under the light microscope.In the ectoderm, epithelio-muscular cells contain various organelles, and also smooth longitudinal muscle-fibres with.
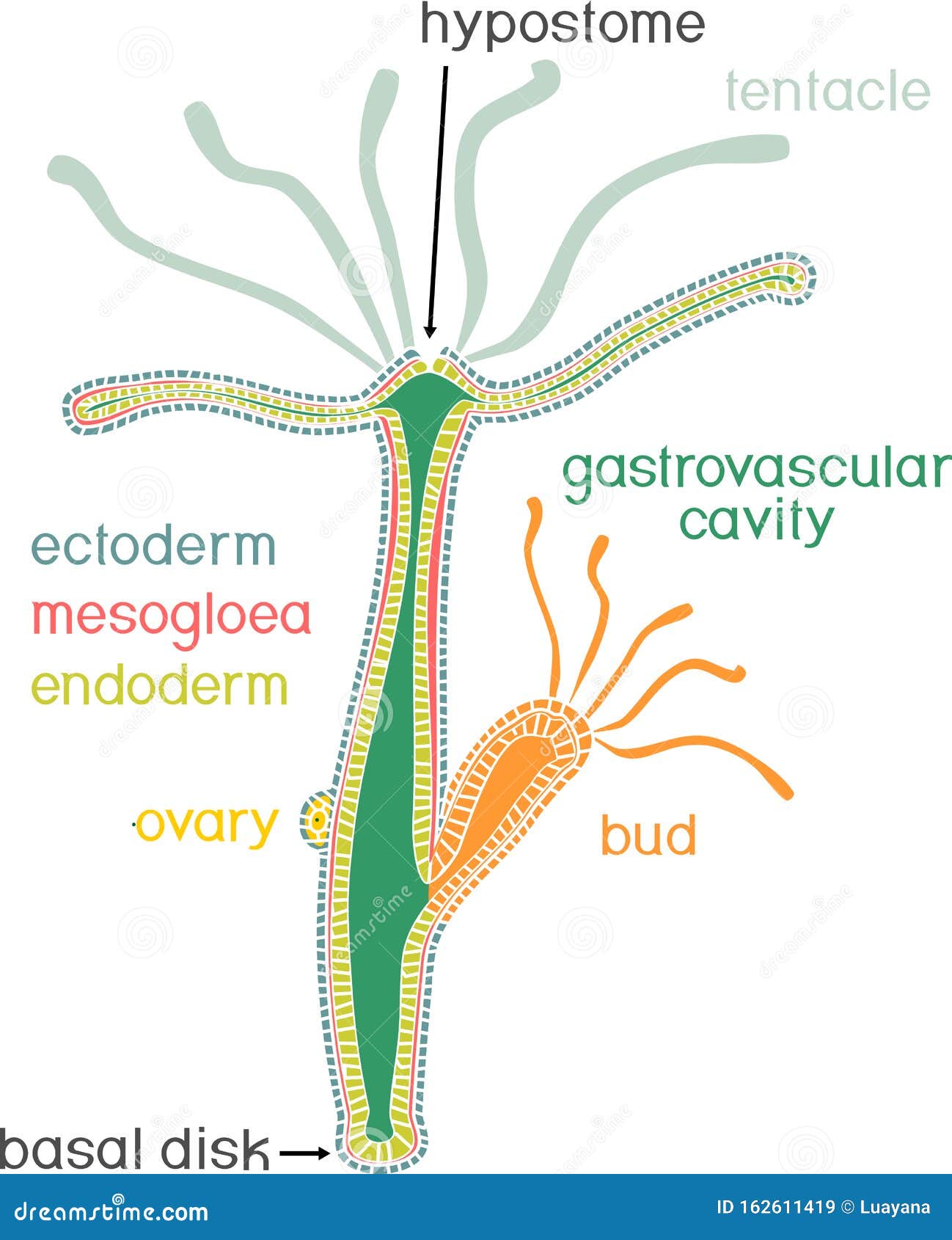
Structure of Hydra. Crosssection of Hydra Polyp Stock Vector
Internal Structure of Hydra (With Diagram) Article Shared by ADVERTISEMENTS: The following points highlight the five main parts that make up the internal structure of Hydra. The parts are: 1. Body Wall 2. Epidermis 3. Gastrodermis 4. Mesogloea 5. Gastro vascular cavity. 1. Body Wall: